How much should I be doing? The best starting point is to look at meeting the Australian Guidlines for Exercise and Physical Activity, which we have discussed previously. But a combination of both aerobic and resistance exercises throughout the week will be most beneficial for both immediate and long term management and control of diabetes. The best thing about exercise, is that we don't need specialised equipment to get started. You can start with aerobic exercises like going out for a walk around a local park, or just around the block. For resistance training it can be exercises like squats, push ups and step ups. As Exercise Physiologist we can help you get moving and stay active with exercise programs that are designed specifically for you, taking into account of your unique goals and needs. There are many ways you can see an EP at Simply Stronger.
Categories All
0 Comments
There are many ways you can see an EP at Simply Stronger.
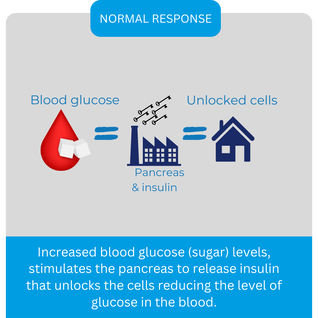
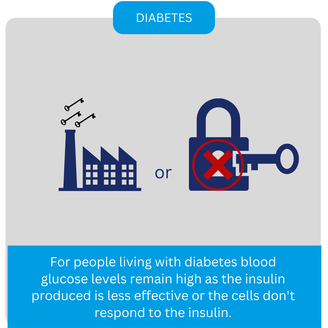
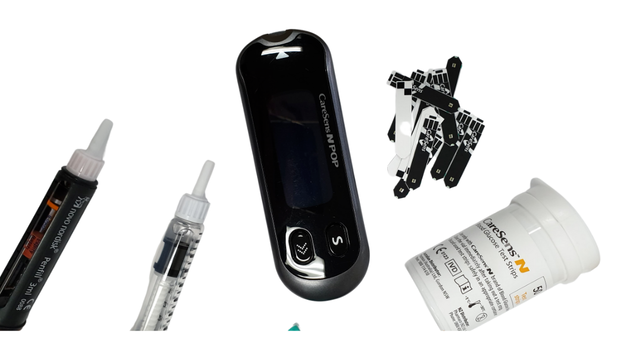
Categories All Blood Glucose? Your blood glucose level is the amount of sugar (glucose) present in your bloodstream. Glucose is the body's main source of energy and comes from the digestion of carbohydrates in our diet. It then gets transported through the blood to different parts of the body for energy production. Having the right level of glucose in your blood is important for your overall health. Our bodies manage our blood glucose levels using hormones called insulin and glucagon, which are produced by the pancreas. When our blood glucose levels are elevated insulin helps lower our levels by moving glucose from the blood into cells. Conversely when more glucose is needed within the blood glucagon raises releases stored glucose from the liver. Normal blood glucose levels can vary, but typically, blood glucose levels will generally sit between 4.0 and 7.8mmol.L (millimoles per litre of blood). Low blood glucose levels, known as hypoglycemia, can occur due to certain medications, underlying health issues or if it has simply been too long since consuming sugar. High blood glucose levels known as hyperglycemia is common in diabetes, where the body doesn't produce enough insulin or doesn't use it effectively resulting in high levels of blood glucose. Prolonged abnormal blood glucose levels can indicate conditions like diabetes, where cells do not react to insulin correctly or become resistant to insulin itself. People with diabetes need to regularly monitor their blood glucose levels. To do this they can use a blood glucose meter which measures glucose levels from a small blood sample obtained by pricking a finger. Monitoring helps them manage their condition by helping them track the impact of diet, exercise, medications, and informed decisions about how to use these along with insulin dosage to keep their blood glucose under control. Next week Coming up next week we explain role exercise plays in managing your blood glucose levels. Categories All |
AuthorSimply Stronger - here to make exercise simple. Understanding why you should exercise is a giant step towards wanting to exercise. Archives
April 2024
Categories
All
|










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed